Pricing
Pricing in Sales and Distribution is used to define the calculation of prices for external vendors or customers and cost. This condition is defined as a set of conditions when a price is calculated.
Example
Consider a case when customer orders specific quantity of a product on a particular day. Various factors like customer, product, order quantity and date tells the final price to that customer. This information is stored in the system as master data in the form of condition records.
There are various pricing elements like prices, surcharges, discounts, and taxes, which are defined in SAP system as condition types. To manage pricing information for a pricing element in a system, you have to create condition records.
Manual Pricing
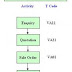
While processing a sales order, you can also manipulate the pricing at the item as well as the header level. Manual processing of a price screen is dependent on individual condition types. During a Sales Order processing using manual processing for a condition type, you can perform the below activities −
- Deleting the pricing element.
- Changing a condition amount.
- Entering additional pricing elements.
How to add Pricing elements manually?
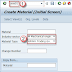
If you want to add customer discount manually in the pricing screen of a sales order, click on Add line. In Data screen, you can enter additional conditions like – customer discount in the condition type field. Enter a percentage range and then press ENTER. You can also delete pricing elements in item pricing and header screens. To do this, select the particular condition by positioning the cursor and click on delete line.
Note that all header conditions defined at header level cannot be changed at the item level, and conditions defined at this level cannot be changed at the header level. Only the Conditions that you define at both header and item conditions can only be edited at both levels.
Condition Record & Table
A Condition table is defined as a combination of keys to identify an individual condition record. A condition record is defined as how system stores the specific condition.
Example of a Condition Record − Entering the price of a product or to specify the discount for a privileged customer.
Example of a Condition Table − Condition records for a customer specific material prices are stored by a sales department. SAP system contains a conditional table 005 for this purpose. Key of table 005 includes the following field −
- Customer
- Material
- Sales Organization
- Distribution Channel
In the first two fields, the customer and material determines the relationship between customers and specific materials. The last two fields are used to identify organization data in a SAP system. Now, if sales department in an organization enters a condition record for discount to one privileged customer, the system will automatically make use of the condition table 005 to store the record and define a key. Any standard SAP system contains predefined condition tables and specifies for each access in a predefined access sequence.
Creating Condition Tables
In a SAP system, you can create or change existing condition tables. As per the new business requirement in an organization, you can create new condition tables.
Go to SPRO → IMG → Sales and Distribution → Basic Functions → Pricing → Pricing Control → Define Conditional Tables
A new window will open and then you can select from create, change or display field as per the requirement. To create a new table, you have to select create and click on
Choose.
Enter condition table in table field and then you can enter the existing table to copy the condition.
Once data is copied, you can modify the table as per the business requirement.
Condition Techniques & Types
Condition type is defined as specific features of daily pricing activities in a SAP system. Using the condition type, you can also put different condition types for each pricing, discounts on goods, tax and surcharge that occurs in business transactions.
Example
Condition type allows you to define the discount for special material. This can be specified in the system to calculate discount as an amount or it can calculate discount in terms of percentage. In case you have to use both discount types, two separate condition types have to be defined in the system.
There are predefined condition types in a standard system −
| S.No | Condition Type & Description |
|---|---|
| 1 |
PR00
Price
|
| 2 |
K004
Material Discount
|
| 3 |
K005
Customer-specific material discount
|
| 4 |
K007
Customer discount
|
| 5 |
K020
Price group discount
|
| 6 |
KF00
Freight surcharge(by item)
|
| 7 |
UTX1
State tax
|
| 8 |
UTX2
Country tax
|
| 9 |
UTX3
City tax
|
How to create or change an existing condition type in a system?
You can change or maintain existing condition type in a standard system. You can also create a new condition types as per business requirements in your organization.
Go to SPRO → IMG → Sales and Distribution → Basic Functions → Pricing → Pricing Control → Define Condition Types
A new window will open. Select maintain and then change as per the requirement and click on Choose.
Once you select Maintain Condition Types and click on Choose, a new window will open. Select a condition type and click on copy.
Enter the name of condition type. Fill the details for Control Data −
- Condition Class (A, B, D, E)
- Condition Type (A-Percentage, B- Amount, C, G)
- Condition Category (Cost, Price, etc.)
- Rounding rule (Commercial, round up, round down)
- Structure Condition
- Plus/Minus
Group Condition data
Changes which can be made
Master Data Section
Scale and Control Data 2 section
Once all the details are entered, click on the save icon at the top.
Pricing
 Reviewed by Unknown
on
August 28, 2017
Rating:
Reviewed by Unknown
on
August 28, 2017
Rating:
 Reviewed by Unknown
on
August 28, 2017
Rating:
Reviewed by Unknown
on
August 28, 2017
Rating:
















No comments